 December 12, 2018
Fabricators / Structural engineers / Student zone
0 Comment
December 12, 2018
Fabricators / Structural engineers / Student zone
0 Comment
Bolts are one of the most common elements in construction and machine design. They consist of fasteners that capture and join other parts, and are secured with the mating of screw threads.
As per AISC We have 3 type of bolts which are commonly used
- ASTM-A325 (Structural Bolts)-Fully tensioned & snug tight-70% of tensile strength of bolt
- ASTM-A490 (Structural bolts)-Fully tensioned & snug tight-70% of tensile strength of bolt
- ASTM-A307 (Common type of bolt-Machine bolt/Unfinished bolt)


In general A connections with a few large diameter fasteners costs less than one of the same capacity with many small diameter fasteners, The fewer the number of holes to be formed and the less installation work needed. Large Diameter fasteners are particularly favorable in connections where shear governs because the load capacity of a fasteners in shear varies with square of the fastener’s diameter.
However, ¾ & 7/8 in diameter fastener are preferred

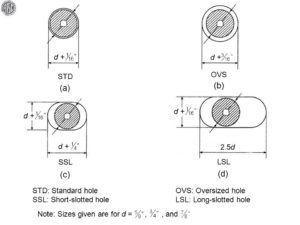
The AISC specification requires that holes for bolts be 1/16 in larger than the nominal fasteners diameter.
In computing net area, the diameter of the hole should be taken 1/16 in larger than the hole diameter.
Holes can be punched or drilled. Punching usually is the most economical method.


SELECTION OF JOINT TYPE
The behavior of the joint and how it affects the structure is the important factor in the proper selection of the joint type.
1.Pre-tensioned joints are used in the following applications:
- Joints that are subject to significant load reversal.
- Joints that are subject to fatigue load with no reversal of the loading direction.
- Joints with ASTM A325 or F1852 bolts that are subject to tensile fatigue.
- Joints with ASTM A490 bolts that are subject to tension or combined shear and tension, with or without fatigue.
2.Column Splices
- Multistory framing>200ft high
- Between 100 to 200 ft height and smaller horizontal dimension of the framing is less than 40% of the height.
- When it is < 100 ft high & smaller dimension is less than 25% of the height.
3.Connections
- Framing 125 ft high on which column bracing is dependent as well as connections of all beams or girders to columns.
- Crane Support, Roof truss splice, truss to column joints, Column splices & bracings, in framing supporting cranes with capacity exceeding 5 tons.
How to Achieve Pre-tension?
- Bolts are bought to snug tight position
- Bolts are then tensioned to 70% of their tensile stress.
- Bolts are tensioned using calibrated wrench, Direct tension indicator

For A490 bolts tensioned to the specified tension, Hardened washers should be used under the head and nut in steel with a specified yield point less than 40 Ksi.
Slip-critical joints are used in the following applications:
- Joints subject to fatigue load with reversal of the loading direction.
- Joints that utilize oversized holes.
- Joints that utilize slotted holes, except those with the applied load approximately normal to the long dimension of the slot.
- Joints in which slip at the faying surfaces would be detrimental to the performance of the structure.
Tightening methods
- Calibrated wrench method.

When Calibrated wrench is used, it must be set to cut off tightening when the required tension has been exceeded by 5%. & Wrench should be calibrated periodically.
- Turn of the nut method

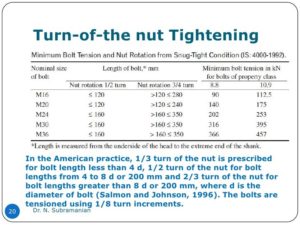
Tightening may be done by impact of hand wrench involves 3 steps
- Fit up of connection: Enough bolts are tightened a sufficient amount to bring contact surface together .This can be done with fit up bolts, But it is more economical to use some of the final high strength bolts
- Snug tightening of bolts: All high strength bolts are inserted and made snug tight
- Nut rotation from snug tight position: All bolts are tightened by the amount of nut rotation
- Direct tension indicator

The direct tension indicator (DTI) hardened steel load indicator washer has dimples on the surface of one face of the washer. When the bolts torqued, the dimples depress to the manufacture’s specification requirements, and proper torque can be measured using feeler gage.
- Alternate design TC bolts

The alternative design bolt (twist off or TC bolts) is a bolt with extension to the actual length of the bolts. This extension will twist off when torque to the required tension by special torque gun.
Bolt cost Comparison

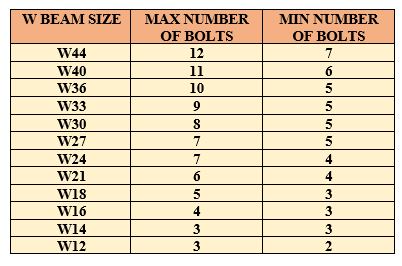
MAXIMUM & MINIMUM NUMBER OF ONE ROW OF BOLTS FOR W-SECTIONS (AS PER AISC)

Design Checks for Bolts (As per AISC Manual 15th edition )
- Check for tension capacity of bolt
Refer AISC manual J3.7
- Check for shear capacity of bolt
Refer AISC Table 7
- Bearing of bolts with Hole
Refer Section J3.10
- Slip resistance
For slip critical connection, Refer Section J3.8
Eccentrically loaded bolts.
- Instantaneous center of rotation.
Its more accurate method to analyze the eccentric connections but it requires lot of iteration.
- Elastic method.
Its easy to compute the calculation & widely used method by connection Engineers.
Soon We will write a article on Elastic method & also Automated excel sheet (VBA) for force calculation.
Regards
StructuralEverest Team
info@structuralEverest.com
Design@structuralEverest.com
www.structuralEverest.com
+91-9964635453

Post a Comment